Python - 단위 테스트 pytest 사용법
파이썬 테스트 도구 : pytest (python ver 3.10)
1. 단위 테스트 (pytest)
TDD (Test Driven Development 테스트 주도 개발) 테스트에 집중하여 개발의 완성도를 높여 나가는 개발론이다. 현재는 다양한 테스트 도구들이 있다. 파이썬으로 개발하면서 파이썬 환경에 맞는 테스트 도구들을 알아보게 되었고, unittest, pytest 에 대해서 정리해보았다.
Unit Test는 유닛 단위, 즉 함수 단위로 테스트 하는 것을 의미한다. 각 단위별로 테스트하면서 이슈 사항을 줄여나간다면 전체적으로 안정적인 개발물에 가까워질 것이다. (에러를 맞이할수록 개발이 더욱 즐거워진다.)
테스트 코드를 작성하면 구현한 함수들이 정상적으로 구현되었는지 확인하는 것 뿐만 아니라, 코드의 흐름, 연관 관계, 기능에 대해서 이해하는데 도움이 된다.
테스트 코드를 작성함에 있어서 편리함도 중요하지만 무엇보다 테스트 결과를 쉽게 눈으로 확인할 수 있는 가시성 도 중요하다. pytest에는 html 파일로 보고서를 만들어주는 기능이 있는데 유용하다. 예제 코드를 통해 기능들을 알아본다.
1.1 pytest, 설치 및 실행 방법
- 설치
pip3 install pytest
- 실행
pytest 실행하려는 파일.py
2. 단위 테스트 리포팅 도구(pytest-html)
pytest-html(테스트 결과를 html 파일로 생성), logging(다양한 옵션으로 디버깅을 지원)을 통해 테스트 결과의 가시성을 높일 수 있는 도구들이 있다.
2.1 pytest-html, 설치 및 실행 방법
- 설치
pip3 install pytest-html
- 실행방법
pytest –html=report/report.html 실행하려는파일.py
pytest –html=report/report.html test_pytestsample.py
2.2 로그
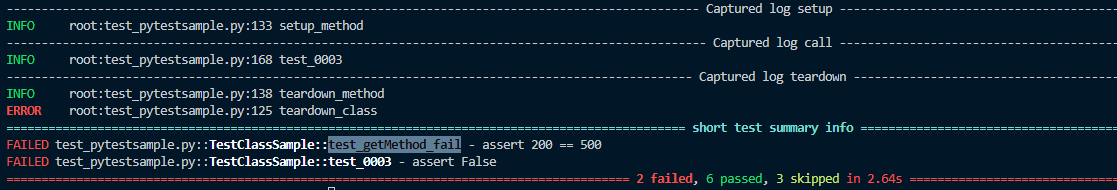
2.3 html 화면
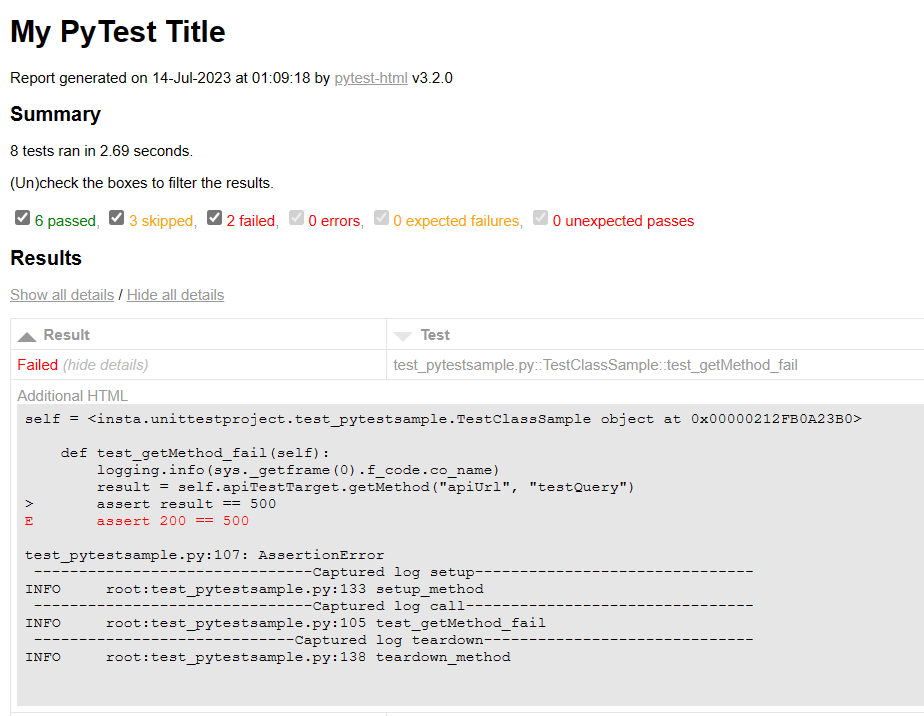
3. pytest 세부 옵션 및 기능
3.1 test_, _test
test_라는 접두사(Prefix)로 시작하는 파일 또는 _test라는 접미사(Suffix)로 끝나는 파일을 찾아서 테스트 코드를 실행하고 그 결과를 화면에 출력
pytest
만 실행했을 때 자동으로 파일을 찾아서 테스트 코드를 실행한다.
https://wikidocs.net/80337
3.3 logging.info 옵션
- sys._getframe(n) : n단계 전의 프레임을 얻음
- sys._getframe(0).f_code.co_name : 현재 실행중인 함수 이름 구하기
- sys._getframe(n).f_locals을 이용하여 해당 프레임의 지역 변수도 접근 가능
3.4 테스트 전 후
- fixture
테스트 함수 실행 전에 개체를 초기화하거나 데이터를 설정하거나 테스트 환경을 구성하는 방법을 제공한다.
- teardown
리소스를 정리하거나 일련의 테스트가 완료된 후 작업을 수행하기 위해 Pytest 프레임워크에서 제공하는 메커니즘이다.
3.5 assert 기능
assert는 뒤의 조건이 True가 아니면 AssertError를 발생한다. 테스트 코드 안에서는 assert 를 사용해서 실제 함수의 반환값이 예상되는 값과 같은지를 확인할 수 있다. unittest는 별도의 assert 구문을 사용하지만, Pytest는 python 기본 내장 함수인 assert()를 사용할 수 있습니다.
형식
assert <표현식> [, '진단 메시지']
assert 조건, ‘메시지’.
‘메시지’는 생략할 수 있다.
3.6 특정 케이스 skip 처리
pytest.mark.skip() 를 사용하면, 해당되는 테스트 함수는 skip 된다.
형식
@pytest.mark.skip(‘스킵 메시지’)
4. 예제 코드
4.1 예제 코드의 구조
Test code는 일반적으로 기존 프로젝트 코드와 다른 디렉토리에 위치하므로 비슷하게 구성하였다.
- 설정
- pytest.ini : pytest 실행시 필요한 설정을 작성한다. (장점) CLI 명령을 사용하여 테스트를 실행할 때마다 테스트 작동 방식을 지정해야되는데 이를 pytest.ini 파일에 기술하여 테스트 실행시마다 옵션을 입력하지 않아도 되도록 한다.
- conftest.py : html report를 생성하기 위한 설정을 기술
- 테스트 대상(클래스, 함수)
- apiConnector.py : 테스트 타겟 클래스(DTO, 구현 함수 등)
- 테스트 코드 작성
- test_pytestsample.py : pytest 테스트 코드를 기술
4.2 test_pytestsample.py
import pytest, sys, logging
from time import sleep
import os
import sys
path = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), os.pardir)
#path = 'D:/~' 안되면 절대경로
sys.path.append(path)
from apiConnector import CRUDConnector, SoftwareTest, SoftwareCategory, ApiFunctions
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Test 1. 함수별(Function Test)
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
'''fixture test case 함수를 실행 "전"에 실행'''
def setup_function(function):
logging.info(sys._getframe(0).f_code.co_name)
'''teardown test case 함수를 실행 "후"에 실행'''
def teardown_function(function):
logging.info(sys._getframe(0).f_code.co_name)
'''assert() 테스트 성공, 실패 판단'''
def test_function_01():
""" Test Function"""
logging.info(sys._getframe(0).f_code.co_name)
assert (True)
def test_function_02():
""" Test Function"""
logging.info(sys._getframe(0).f_code.co_name)
assert (True)
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
# Test 2. 클래스(Class Test)
# ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
class TestClassSample():
#@pytest.fixture 이 어노테이션을 사용하면, 테스트 실행 전에 이 함수를 실행하여 값이나 리소스에 필요한 준비 작업을 할 수 있다.
@pytest.fixture
def serial_tester(self):
logging.info(sys._getframe(0).f_code.co_name)
return CRUDConnector()
@pytest.fixture(autouse=True) #클래스 내의 모든 테스트 메서드에서 픽스처가 자동으로 사용
def setUp(self):
self.apiTestTarget = ApiFunctions()
@pytest.fixture
def post_serial(self, serial_tester):
logging.info(sys._getframe(0).f_code.co_name)
tester = serial_tester.create_serial()
yield tester
serial_tester.delete_serial(tester)
@pytest.fixture
def get_serial(self, serial_tester):
logging.info(sys._getframe(0).f_code.co_name)
tester = serial_tester.create_serial()
yield tester
tester.clear_serial()
serial_tester.delete_serial(tester)
#assert 테스트 성공, 실패 판단
def test_serial_get(self, post_serial, get_serial):
logging.info(sys._getframe(0).f_code.co_name)
serial = SoftwareCategory(name='test', version='1.0')
post_serial.send_serial(serial, get_serial)
assert serial in get_serial.category
def test_getMethod_pass(self):
logging.info(sys._getframe(0).f_code.co_name)
result = self.apiTestTarget.getMethod("apiUrl", "testQuery")
assert result == 200
def test_getMethod_fail(self):
logging.info(sys._getframe(0).f_code.co_name)
result = self.apiTestTarget.getMethod("apiUrl", "testQuery")
assert result == 500
def test_postMethod(self):
logging.info(sys._getframe(0).f_code.co_name)
result = self.apiTestTarget.postMethod("apiUrl", "testQuery")
assert result == 433
# @classmethod : 클래스 메서드 사용하며, cls 키워드를 사용한다. (self 와의 차이 : self는 인스턴스 메서드)
@classmethod
def setup_class(cls):
""" setup any state specific to the execution of the given class (which usually contains tests)."""
logging.info(sys._getframe(0).f_code.co_name)
cls.name= 'test'
cls.members = [1, 2, 3, 4]
@classmethod
def teardown_class(cls):
""" teardown any state that was previously setup with a call to setup_class."""
logging.error(sys._getframe(0).f_code.co_name)
pass
def setup_method(self, method):
""" setup any state tied to the execution of the given method in a class.
setup_method is invoked for every test method of a class.
"""
logging.info(sys._getframe(0).f_code.co_name)
def teardown_method(self, method):
""" teardown any state that was previously setup with a setup_method call.
"""
logging.info(sys._getframe(0).f_code.co_name)
def test_0001(self):
logging.info(sys._getframe(0).f_code.co_name)
sleep(1)
assert (True)
'''특정 테스트 케이스를 skip'''
# @pytest.mark.skip 는 테스트를 건너뛰도록 지정
# https://docs.pytest.org/en/7.1.x/how-to/skipping.html
@pytest.mark.skip("Do not run this testcase")
def test_fail():
assert False
# reason은 테스트를 건너뛰는 이유를 설명하는 문자열
@pytest.mark.skip(reason="Skip reasson")
def test_0002(self):
logging.info(sys._getframe(0).f_code.co_name)
sleep(1)
assert (True)
# skipif()는 조건부로 무언가를 건너뛰도록 지정
testData = None
@pytest.mark.skipif(testData is None, reason="testData is None")
#@pytest.mark.skipif(sys.version_info < (3, 10), reason="requires python3.10 or higher")
def test_chkTestData():
assert (True)
def test_0003(self):
logging.info(sys._getframe(0).f_code.co_name)
sleep(1)
assert (False)
@pytest.mark.mandatory
def test_mandatory(self):
logging.info(sys._getframe(0).f_code.co_name)
assert True
# pytest_sessionfinish : 테스트 세션을 끝낼 때 호출
class MyPlugin:
def pytest_sessionfinish(self):
pass
if __name__ == "__main__":
# args_str = '--html=report/report.html --self-contained-html '+ __file__
# args_str = ' --capture=tee-sys '+ __file__
args_str = '--html=report/report.html ' + __file__ # html report 생성
args = args_str.split(" ")
pytest.main(args, plugins=[MyPlugin()]) # 플러그인 추가
# pytest.main(args)
apiConnector.py (테스트 대상이 되는 클래스)
import os
import sys
path = os.path.join(os.path.dirname(__file__), os.pardir)
#path = 'D:/프로젝트명' #안되면 절대경로 지정
sys.path.append(path)
#DTO 클래스
class SoftwareCategory:
def __init__(self, name, version):
self.name = name
self.version = version
class CRUDConnector:
def create_serial(self):
return SoftwareTest()
def delete_serial(self, tester):
# do some cleanup
pass
class SoftwareTest:
def __init__(self):
self.category = []
def send_serial(self, serial, software):
software.category.append(serial)
def clear_serial(self):
self.category.clear()
class ApiFunctions:
def getMethod(self, x, y):
if x == "apiUrl" and y == "testQuery":
return 200
else:
return 400
def postMethod(self, x, y):
if x == "apiUrl" and y == "testQuery":
return 433
else:
return 400
4.3 pytest.ini
테스트 파일 실행시 옵션을 명령어에 작성하지 않아도 이곳에서 작성하면 적용이 된다. pytest.ini 테스트 파일로 인식할 파일, 기본 실행할 명령어 옵션을 설정할 수 있다.
전체 테스트 중 반드시 실행해야할 테스트는 ‘mandatory’로 mark 설정할 수 있다.
그리고 명령어에 다음 옵션을 넣어 실행하면, mark된 함수만 실행된다.
pytest -m mandatory
설정 설명
%(levelname)s : 로그 레벨 %(asctime)s : 시간(log_cli_date_format 형태로 출력) %(filename)s : 파일명 %(funcName)s : 함수명 %(lineno)d : logging call이 발생한 코드의 라인 번호 %(name)s : 로그명, 기본값은 root %(levelname)s : 로그 레벨 %(message)s : 로그 메세지
pytest.ini
[pytest]
log_cli=true
log_cli_level=DEBUG
log_cli_date_format=%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S
#log_format = %(asctime)s %(levelname)s %(message)s
log_cli_format=%(levelname)-8s %(asctime)s %(name)s::%(filename)s:%(funcName)s:%(lineno)d: %(message)s
markers = mandatory: mark tests that should be executed
4.4 conftest
html 파일 생성 및 설정
pytest –html=report.html –self-contained-html
pytest –html=report/report.html test_pytestsample.py
conftest.py
from datetime import datetime
from py.xml import html
import pytest
import sys
import logging
'''보고서 제목'''
def pytest_html_report_title(report):
report.title = "My PyTest Title"
pass
'''요약 섹션을 편집'''
#@pytest.mark.optionalhook
pytest.hookimpl(optionalhook=True)
def pytest_html_results_summary(prefix, summary, postfix):
# prefix.extend([html.h3("Adding prefix message")])
# summary.extend([html.h3("Adding summary message")])
# postfix.extend([html.h3("Adding postfix message")])
pass
'''테스트를 실행하기 전에 환경 섹션을 수정'''
def pytest_configure(config):
# print(sys._getframe(0).f_code.co_name)
# # getting user name
# from pwd import getpwuid
# from os import getuid
# username = getpwuid(getuid())[0]
# # getting python version
# from platform import python_version
# py_version = python_version()
# # overwriting old parameters with new parameters
# config._metadata = {
# "user_name": username,
# "python_version": py_version,
# "date": "오늘"
# }
pass
@pytest.hookimpl(hookwrapper=True)
def pytest_runtest_makereport(item, call):
pytest_html = item.config.pluginmanager.getplugin('html')
outcome = yield
report = outcome.get_result()
extra = getattr(report, 'extra', [])
if report.when == 'call':
# always add url to report
# extra.append(pytest_html.extras.url('./assets/image.png'))
#extra.append(pytest_html.extras.text(item.name))
# extra.append(pytest_html.extras.text('some string', name='Different title'))
xfail = hasattr(report, 'wasxfail')
if (report.skipped and xfail) or (report.failed and not xfail):
# only add additional html on failure
extra.append(pytest_html.extras.html('<div>Additional HTML</div>'))
report.extra = extra
참고
fixtures https://docs.pytest.org/en/7.4.x/reference/fixtures.html#fixtures skip https://docs.pytest.org/en/7.1.x/how-to/skipping.html pytest html report https://pytest-html.readthedocs.io/en/latest/user_guide.html pytest option https://docs.pytest.org/en/6.2.x/reference.html#command-line-flags pytest.ini https://pytest-with-eric.com/pytest-best-practices/pytest-ini/

댓글남기기