인공지능 - NLP (5) 텍스트 분류 작업에 대한 DNN, CNN, RNN 및 GRU 모델의 비교 분석
텍스트 분류 작업에 대한 DNN, CNN, RNN 및 GRU 모델의 비교 분석을 위한 예제 코드의 내용과 출력된 그래프의 의미를 설명드리겠습니다.
코드 설명
- 데이터 전처리:
- 텍스트 데이터를 정수 시퀀스로 변환하고 시퀀스의 길이를 맞추기 위해 패딩을 추가합니다.
- 학습 레이블은 원-핫 인코딩으로 변환됩니다.
- 모델 정의:
- 네 종류의 모델을 정의합니다:
- DNN (Deep Neural Network): 간단한 밀집 신경망 구조로 텍스트 임베딩 후 Flatten 레이어와 여러 Dense 레이어로 구성됩니다.
- CNN (Convolutional Neural Network): 텍스트 임베딩 후 1차원 합성곱 및 맥스 풀링 레이어로 특징을 추출하는 모델입니다.
- RNN (Recurrent Neural Network): LSTM 레이어를 사용하여 순차 데이터(텍스트)를 처리하는 모델입니다.
- GRU (Gated Recurrent Unit): LSTM과 유사하지만 더 간결한 구조를 가지는 순환 신경망 모델입니다.
- 네 종류의 모델을 정의합니다:
- 모델 학습 및 평가:
- 각 모델에 대해 학습을 진행하고 학습 데이터에 대한 정확도를 계산합니다.
- 각 모델의 학습 정확도를 비교하여 결과를 출력하고 시각화합니다.
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings("ignore", category=UserWarning)
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.layers import Dense, Dropout, Embedding, Flatten, Conv1D, MaxPooling1D, LSTM, GRU
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.text import Tokenizer
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.sequence import pad_sequences
from tensorflow.keras.utils import to_categorical
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def preprocess_texts(train_texts, train_labels, new_texts, num_words=1000, max_len=20):
"""
Converts text data into integer sequences and applies padding for model input preparation.
Args:
train_texts (list): Training text data.
train_labels (list): Labels for training data.
new_texts (list): New text data for prediction.
num_words (int): Maximum number of words to use.
max_len (int): Maximum length of sequences.
Returns:
tuple: Preprocessed training data (x_train, y_train) and new data (x_new).
"""
tokenizer = Tokenizer(num_words=num_words)
tokenizer.fit_on_texts(train_texts)
x_train = tokenizer.texts_to_sequences(train_texts)
x_new = tokenizer.texts_to_sequences(new_texts)
x_train = pad_sequences(x_train, maxlen=max_len, padding='post')
x_new = pad_sequences(x_new, maxlen=max_len, padding='post')
y_train = to_categorical(train_labels, 2) # Convert labels to one-hot encoding
return x_train, y_train, x_new
def train_and_evaluate_model(model, x_train, y_train):
"""
Trains and evaluates a model.
Args:
model (Sequential): Model to train.
x_train (array): Training data.
y_train (array): Training labels.
Returns:
tuple: Training history and model accuracy.
"""
model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss='categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])
history = model.fit(x_train, y_train, epochs=10, batch_size=2, verbose=0)
scores = model.evaluate(x_train, y_train, verbose=0)
return history, scores[1]
def build_dnn_model(input_dim, max_len):
"""
Builds a simple DNN model.
Args:
input_dim (int): Dimension of input data (number of words).
max_len (int): Maximum length of input sequences.
Returns:
Sequential: Defined DNN model.
"""
model = Sequential()
model.add(Embedding(input_dim=input_dim, output_dim=128, input_length=max_len))
model.add(Flatten())
model.add(Dense(128, activation='relu'))
model.add(Dropout(rate=0.5))
model.add(Dense(64, activation='relu'))
model.add(Dense(2, activation='softmax'))
return model
def build_cnn_model(input_dim, max_len):
"""
Builds a CNN model with Conv1D and MaxPooling1D layers.
Args:
input_dim (int): Dimension of input data (number of words).
max_len (int): Maximum length of input sequences.
Returns:
Sequential: Defined CNN model.
"""
model = Sequential()
model.add(Embedding(input_dim=input_dim, output_dim=128, input_length=max_len))
model.add(Conv1D(128, 5, activation='relu'))
model.add(MaxPooling1D(pool_size=2))
model.add(Flatten())
model.add(Dense(64, activation='relu'))
model.add(Dense(2, activation='softmax'))
return model
def build_rnn_model(input_dim, max_len):
"""
Builds an RNN model with an LSTM layer.
Args:
input_dim (int): Dimension of input data (number of words).
max_len (int): Maximum length of input sequences.
Returns:
Sequential: Defined RNN model.
"""
model = Sequential()
model.add(Embedding(input_dim=input_dim, output_dim=128, input_length=max_len))
model.add(LSTM(128))
model.add(Dense(64, activation='relu'))
model.add(Dense(2, activation='softmax'))
return model
def build_gru_model(input_dim, max_len):
"""
Builds a GRU model.
Args:
input_dim (int): Dimension of input data (number of words).
max_len (int): Maximum length of input sequences.
Returns:
Sequential: Defined GRU model.
"""
model = Sequential()
model.add(Embedding(input_dim=input_dim, output_dim=128, input_length=max_len))
model.add(GRU(128))
model.add(Dense(64, activation='relu'))
model.add(Dense(2, activation='softmax'))
return model
# Preparing data
# Example text data and labels for training and testing
train_texts = ["이 음식은 정말 맛있습니다", "별로 맛이 없어요", "이 음식을 추천합니다", "맛이 매우 별로입니다"]
train_labels = [1, 0, 1, 0]
new_texts = ["이 음식 정말 대단해요!", "돈이 아까워요."]
# Preprocess data
x_train, y_train, x_new = preprocess_texts(train_texts, train_labels, new_texts)
# Define a list of models to train and evaluate
models = [
("DNN", build_dnn_model(1000, 20)),
("CNN", build_cnn_model(1000, 20)),
("RNN", build_rnn_model(1000, 20)),
("GRU", build_gru_model(1000, 20))
]
# Dictionary to store results
results = {}
# Train and evaluate each model
for name, model in models:
print(f"{name} 모델 학습 중...")
history, accuracy = train_and_evaluate_model(model, x_train, y_train)
results[name] = (history, accuracy)
# Compare and visualize results
for name, (history, accuracy) in results.items():
print(f"{name} 모델 - 학습 정확도: {accuracy * 100:.2f}%")
# Plotting the training accuracy of each model
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 5))
for name, (history, _) in results.items():
plt.plot(history.history['accuracy'], label=f'{name} Accuracy')
plt.title('Model Accuracy Comparison')
plt.xlabel('Epoch')
plt.ylabel('Accuracy')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
그래프 설명
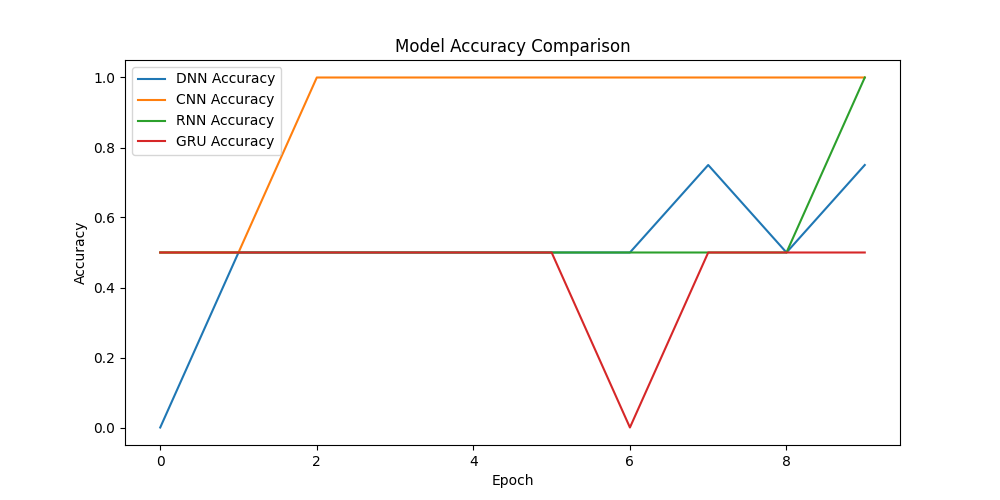
- 그래프는 각 모델의 에포크에 따른 학습 정확도를 시각화한 것입니다.
- DNN, CNN, RNN 모델의 학습 정확도는 점차 증가하여 최종적으로 100%에 도달했습니다. 이는 학습 데이터에서 모든 샘플을 정확히 분류했음을 의미합니다.
- GRU 모델의 학습 정확도는 50%로 낮게 유지되었고, 학습 과정에서 전혀 개선되지 않았습니다. 이는 이 모델이 주어진 데이터셋에서 적절히 학습하지 못했음을 나타냅니다.
그래프 해석
- DNN과 CNN 모델은 빠르게 100% 정확도에 도달하며 안정적인 학습 과정을 보입니다.
- RNN 모델은 중간에 급격한 변동이 있지만 최종적으로 100% 정확도에 도달합니다.
- GRU 모델은 전혀 학습되지 않는 모습으로 학습 초반부터 50%의 정확도를 유지하며 학습에 실패한 것으로 보입니다. 이는 데이터가 매우 단순하거나 GRU가 이 데이터셋에 적합하지 않을 수 있습니다.
이 결과는 각 모델이 간단한 데이터셋에 대해 어떻게 학습하는지를 보여주며 일부 모델이 해당 데이터셋에서 학습하지 못하는 모습을 명확히 나타내고 있습니다.

댓글남기기