Shallow Copy vs. Deep Copy in JAVA
What Are Shallow Copy vs. Deep Copy?
1. The Definition of Copy
to produce something so that it is the same as an original piece of work. (Cambridge English Dictionary)
"To create something identical to the original work."
If a copy is created from the original but modifying the copy affects the original, it isn’t a true copy in the real sense.
2. Shallow Copy vs. Deep Copy
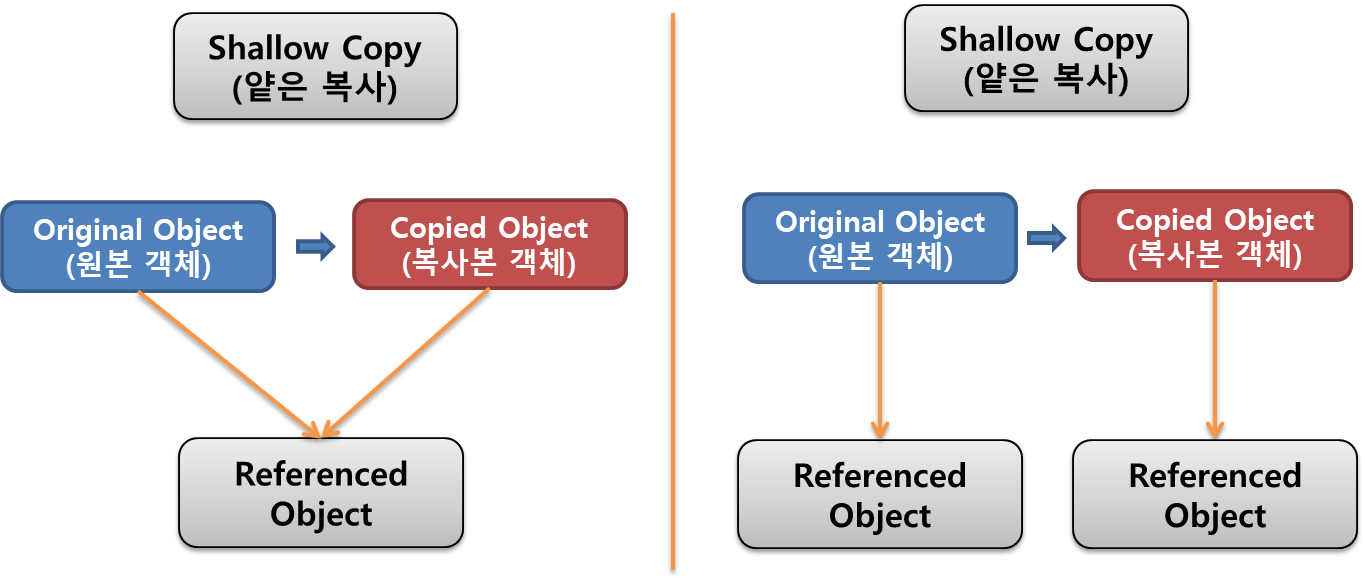
Shallow Copy refers to copying the ‘memory address’ stored by reference type data. Even though the variable is copied, the reference remains the same, pointing to the same memory. The copied object shares the original object.
In shallow copy, changing the value in one variable affects the other because only the ‘reference’ is copied, not the actual data.
Deep Copy creates a completely independent copy by allocating new memory space. The original and copied objects are distinct and independent of each other, representing a more genuine form of copying.
3. What Are Primitive and Reference Types?
- Primitive Types: null, undefined, string, number, boolean, symbol.
- Reference Types: Array, Object, Function.
4. Primitive Type Data
- Primitive types directly access the memory area where values are stored when declared, initialized, or assigned. When a new value is assigned to a variable, it directly changes the value stored in the memory block assigned to the variable.
- Assigning a new value to a variable changes the address of the memory space referenced by the variable.
- It is stored in a fixed size in memory when assigned, and the variable holds the value of the primitive data directly.
- The value is copied to create a new one (true copying).
5. Reference Type Data
- Instead of manipulating the object’s memory directly, reference type data manipulates the ‘reference’ to the object, accessing values via the reference.
- Reference types do not have a fixed size and cannot directly store their values in the variable when assigned; instead, the variable stores only the reference to the data.
- It accesses the variable via the memory address of the value.
Implementing Deep Copy in JavaScript
You can implement a deep copy using JSON.stringify() and JSON.parse().
- JSON.stringify() converts a JSON type object to a string type (primitive type).
- JSON.parse() converts a string type (primitive type) back to a JSON type (reference type).
Since strings are primitive types, not reference types, they inherently ‘copy the value itself’ rather than copying the address.
(Example)
const OriginalObj = {
dataA: 111,
dataB: {
dataC: 222,
},
};
const newObj = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(OriginalObj));
newObj.dataB.dataC = 333;
console.log(OriginalObj.dataB.dataC); // 222
console.log(newObj.dataB.dataC); // 333
// Comparing values
console.log(OriginalObj === newObj); // false

댓글남기기